Answer:
To produce speech sounds, different organs play an active role. They are known as the organs of speech. From breathing in the air to breathing out into the atmosphere, these organs help to produce speech sounds that we need for communication. These organs are divided into three groups. Those are-
- The respiratory system: lungs, muscles, bronchial tube, trachea.
- The phonatory system: larynx, vocal cords.
- The articulatory system: nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, and lips.
Lungs:
It is a bladder-like spongy organ filled with air made up of alveoli. It is located on both sides of the chest. When we breathe in, the air passes through the throat into the lungs through the trachea, also known as the bronchial tube. After that, the muscles inside the lungs expand and contract by ingression or egression of air. The air stream related to the lungs is called the pulmonic airstream mechanism. It has two parts- an aggressive air stream mechanism and an ingressive airstream mechanism. Speech sounds are produced by an aggressive air stream mechanism. The ingressive airstream mechanism is responsible for producing non-linguistic sounds like yawning, snoring, clicking, etc.
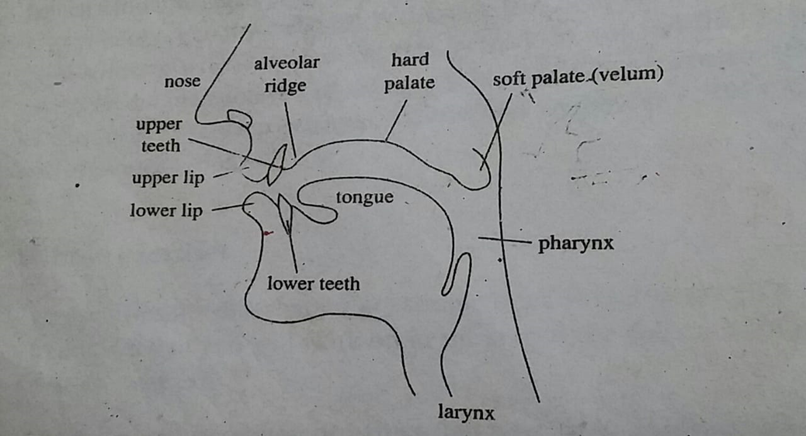
Larynx:
Behind Adam’s apple, the larynx is located. Vocal cords are a part of the larynx. So the organ is often referred to as the sound box. In the larynx, the vocal cords make a structure called arytenoids cartilages. These vocal cords are held wide apart to let the air pass freely. Voiceless sounds like /f, s, and p/ are produced through this process. On the other hand, when the vocal cords are held together, the voiced sounds are produced.
Pharynx:
The pharynx is a tube that begins above the larynx. It is about 7cm long in women and about 8cm in men. At the top, it is divided into two parts- the oral cavity and the nasal cavity.
Soft palate or Velum:
It allows the air to pass through the nose and mouth. It helps in producing sounds like k and g. here, the tongue gets in contact with the lower side of the soft palate, so these sounds are called velar consonants. Also, it is one of the articulators that the tongue can touch.
Hard palate:
it is also known as the “roof of the mouth”. The smooth curved surface can be felt through the tongue inside the mouth. The consonant that is produced with the tongue getting close to the hard palate is a palatal consonant. /j/ in ‘yes’ is a palatal consonant.
Alveolar Ridge:
It is between the top front teeth and the hard palate. It can be felt by the tongue. Its surface is rough and covered with little ridges. Sounds such as t,d, and n are called alveolar sounds.
Tongue:
The tongue is a very important articulator. It can be moved to different places and shapes that help other articulators to do their jobs. It has different parts such as the tip, blade, front, and back.
Teeth:
Teeth are of two types- upper and lower. They are located at the front of the mouth and just behind the lips. Most of the speech sounds are produced when the tongue gets into contact with the upper teeth. The dental sounds are / θ, ð/.
Lips:
Lips are multifunctional in producing speech sounds. They are pressed together while producing sounds like p and b. they are brought into contact with the teeth of articulate f and v. to produce the vowel (u:), and they get rounded. Also, bilabial sounds are produced when the lips are in contact with each other. When the lip and the teeth contribute together, those sounds are called labiodental.
Nasal cavity:
The nose and nasal cavity do not have an active role in producing speech sounds. But they are important equipment for making sounds. It is a structure in the form of a cavity that has two openings at the end part. They are known as nostrils. M and n are nasal sounds.
These are the main organs that help in producing speech sounds.
 CSP
CSP